Articles
Something is Wrong With Gann Angles
When we measure a correctly drawn 1×4 line with a protractor or use the tangent function on a calculator, we get 14.03 degrees. Gann said it was 15 degrees. A 1×2 line is 26.56 degrees yet called 26.25. Everyone just copies Gann’s numbers, but couldn’t he just as easily have said the 1×2 was 26.5 and the 1×4 was 14 degrees. Why the discrepancy, couldn’t Gann count?
 Gann’s geometric angles are proportional parts of the 360 degree circle and used to measure time and space. The circle and the unique numbers of 1 thru 9 were the basis for all his calculations. Using fixed rate of movement trendlines is an easy way to measure this relationship of price to time. It is because of this convenience, there are slight variations in the numbers. To find the various Gann angles, on a properly scaled chart, all we do is count the squares up and over. These angles measure the ratio of how much price has moved in a specific time. For example a $5 move in 20 days, has the ratio of 5 to 20 and equal to a 1×4 line. We can use different proportions such as the following:
Gann’s geometric angles are proportional parts of the 360 degree circle and used to measure time and space. The circle and the unique numbers of 1 thru 9 were the basis for all his calculations. Using fixed rate of movement trendlines is an easy way to measure this relationship of price to time. It is because of this convenience, there are slight variations in the numbers. To find the various Gann angles, on a properly scaled chart, all we do is count the squares up and over. These angles measure the ratio of how much price has moved in a specific time. For example a $5 move in 20 days, has the ratio of 5 to 20 and equal to a 1×4 line. We can use different proportions such as the following:
| Angle | Price units | Time units | Gann Angles |
| 1 x 4 | 1 | 4 | 15.0 |
| 1 x 2 | 1 | 2 | 26.25 |
| 1 x 1 | 1 | 1 | 45.0 |
| 2 x 1 | 2 | 1 | 63.75 |
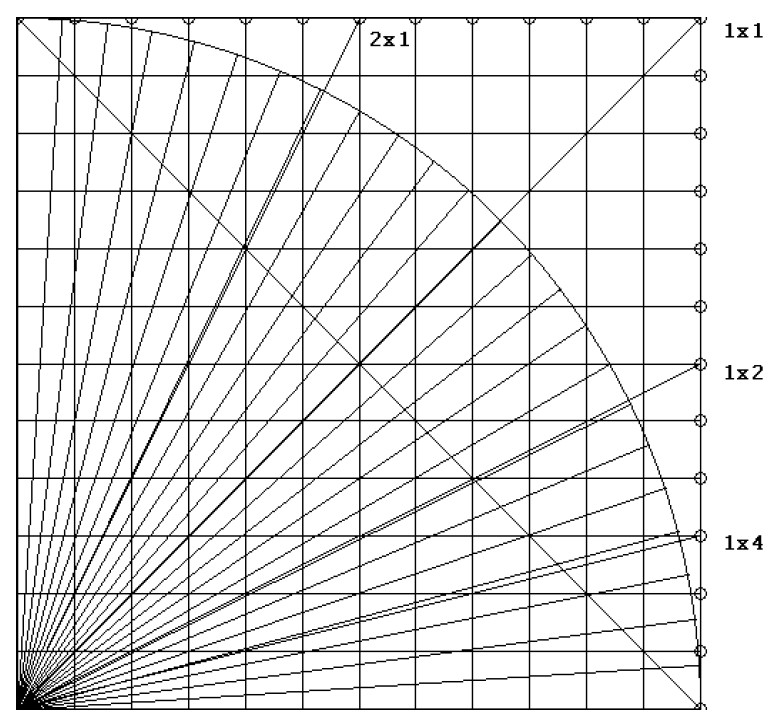
On the chart below, one quarter of a circle, 90 degrees, is drawn on a 12 by 12 square background grid. This circular arc is also divided in 24 even parts of 3.75 degrees each.
The 90 degree angle is used, because it is the strongest. It is vertical, straight up and down like the sun at noontime. The trigonomic proportions of sine, cosine and tangent for the first 90 degrees are unique. Then they are mirrored and repeated for the rest of the circle sometimes with their signs reversed depending on which circle quadrant they are in.
From the lower left corner starting point on the chart, 4 lines are drawn thru the arc and extended to the square’s perimeter. Counting the number of squares shown will give the correct Gann angle line and their actual calculated degrees using the Tangent function, or more correctly the ArcTangent from a calculator.
| Angle | Price | Time | ArcTan |
| 1 x 4 | 3 | 12 | 14.03 |
| 1 x 2 | 6 | 12 | 26.56 |
| 1 x 1 | 12 | 12 | 45.0 |
| 2 x 1 | 12 | 6 | 63.43 |
It is easier to count squares or have our computers use the tangent function. Although the results are close to true Gann angles, they would be more suited if we were measuring on a square grid. But Gann did just as he always said and was thinking in proportionate parts of the circle. In this case 90 degrees is divided into 24 parts of 3.75 degrees each as shown by the 24 lines hitting the circles circumference. You can see how close the 4 extended lines are to them. That is the difference. The 1×4 Gann angle of 15 degrees is the 4th line on the circle (4 times 3.75 = 15) and just above the 1×4 tangent line of 14.03. The 1×2 line is the 7th line and the 2×1 is the 17th line on the circle. Both lines come out equal at 45 degrees, the tangent is 1 and 12 times 3.75 = 45.
Gann was a master mathematician, who knew the difference between convenience and hard work, with enough fingers and toes to count correctly from 1 to 9 and beyond. He also counted on human nature not changing, to supposedly hide some of his secrets in the best place possible – right in front of our face. Although this topic was a minor unquestioned nuance, it is our assumptions and perspectives that helps perpetuate the mystique.
✅ Gann Methodology – Top Ebooks
Here are a few related observations. If we had used a background grid of 17×17, or 289 small squares (very close to 144 times 2), the upward 1×1 line hits the circle almost perfectly at 12 lines up and 12 over. Since dividing squares into eighths is common, and so is the 8×8 to an inch paper scaling, then using 90 degrees as the basis each eighth would be 11.25 degrees or 3 times 3.75 degrees. Even the diagonal on an 8×8 square measures 11.3 units which is also close to 11.25.
One last angle would be to draw the 2 diagonals (the 1×1 lines up and down) on any square. This will create 4 triangles. Using the idea that if price is above a 45 degree line (1×1) it is strong and below it is weak, then only the upper triangle is always strong and the lower triangle is always weak.
Gann always talked about squaring price with time. With that area he added volume, trading activity was not to be taken lightly, but in depth. These points of balance would then help define a markets larger solid structure. Squaring the circle was of great interest, to harmonically bringing the heavens down to earth or maybe coordinating the rectangular to polar. With “use all my rules” his measurements in and out, ruled over what was always here and is here, before us. So obviously, Gann could count, but I wonder why he couldn’t write right!




